20.109(S24):Module 1
Contents
Module 1: drug discovery
Small molecules, or ligands, are important research tools used to explore cellular processes and therapeutic targets. The use of high-throughput and unbiased strategies to identify small molecules that bind specific biomolecules, such as proteins, can provide insight on the structure or function of targets. Additionally, a small-molecule screen can identify new chemical probes for target proteins of interest.
The small-molecule microarray (SMM) is a high-throughput method that enables the detection of protein-ligand binding. Briefly, ligands are 'printed' onto a slide and incubated with purifed protein. Unbound protein is washed from the slide and bound protein is detected using a tag on the protein of interest. Because the location of every ligand on the slide is known, the detection of protein indicates that it is bound to the ligand at that location.
In the Sp23 semester, previous 109ers leveraged the SMM technology to identify small molecules that putatively bind MAX (myc-associated factor X), a protein target relevant in cancer research. The MAX protein contains the basic helix-loop-helix and leucine zipper motifs and functions as a transcription factor in humans. In this role, it forms homodimers and heterodimers with other transcriptional factors. Notably MAX dimerizes with Myc, an oncogenic transcription factor. Because this dimerization is required for Myc to act as a transcription factor, inhibitors of this process are clinically relevant and may lead to the development of a drug therapy to treat cancer. Students identified several putative small molecule binders. For the Sp24 semester, you will test the putative small molecule binders using two functional assays. The assays will 1) confirm binding, and 2) examine the biological significance of binding.
Research goal: Test small molecules that putatively bind to MAX using functional assays.
Lab links: day by day
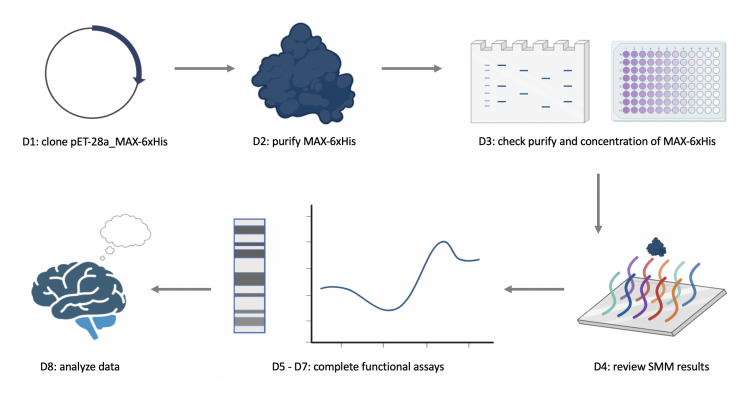
M1D1: Complete in-silico cloning of protein expression vector
M1D2: Purify expressed protein
M1D3: Assess purity and concentration of expressed protein
M1D4: Review results of small molecule microarray (SMM) screen
M1D5: Setup differential scanning flourimetry (DSF) experiment
M1D6: Prepare cells for electromobility shift assay (EMSA)
M1D7: Complete EMSA experiment
M1D8: Evaluate experimental results
Major assignments
References
- A method for the covalent capture and screening of diverse small molecules in a microarray format. Nature Protocols. 1:2344-2352.
- Recent discoveries and applications involving small-molecule microarrays. Chemical Biology. 18:21-28.