20.109(S17):Assess cell survival and harvest RNA for quantitative PCR assay (Day3)
Contents
Introduction
Measuring gene expression provides information on the mechanisms used by cells to respond to stimuli.
nucleic acid purification
reverse transcription
Protocols
Part 1: Workshop with BE Communication Lab
Our communication instructor, Dr. Diana Chien, will join us today for a workshop on transforming a written journal article into a well-defined oral presentation.
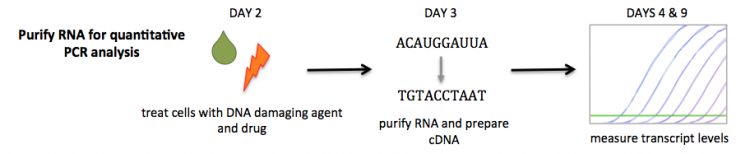
Part 2: Prepare samples for quantitative PCR assay
You will complete the first part of this exercise in tissue culture and then move into the main laboratory to purify the RNA from your cells. Before you begin your work in tissue culture, prepare your laboratory bench for work with RNA. As noted in the introductory material, RNA is very sensitive to degradation and caution must be taken to preserve your sample.
First, obtain a piece of absorbent paper. This will by your RNAse free work space. Spray the absorbent paper with RNase Away and dry with a Kimwipe. Perform this cleaning procedure with all of the equipment you will need for the RNA purification protocol (read through Part 2a Step #11 to the end of the protocol). Also, obtain all of the aliquots you will need from the front laboratory bench and clean before placing the tubes on the absorbent paper work space. Lastly, obtain a 50 mL conical tube and label it 'waste'.
Part 2a: Purify RNA from cells
- Prepare your working space within the tissue culture hood.
- Retrieve your four T25 flasks (DLD-1 +etop, BRCA2- +etop, DLD-1 +etop +drug, and BRCA2- +etop +drug) from the 37 °C incubator and visually inspect your cells with a microscope.
- Record your observations concerning media color, confluency, etc. in your laboratory notebook.
- Aspirate the media from each flask.
- Wash the cells by adding 3 mL PBS using a 5 mL pipet. Slightly tip the flask back and forth to rinse the cells then aspirate the PBS with a fresh Pasteur pipet.
- With a 2 mL pipet, add 1 mL of trypsin to each flask.
- Tip the flask in each direction to distribute the trypsin evenly then incubate the cells at 37°C for 10 minutes using a timer.
- Retrieve your flasks from the incubator and firmly tap the bottom 5 times to dislodge the cells.
- Check your cells using the microscope to ensure they are dislodged. They should appear round and move freely.
- If your cells are not detached from the flask, incubate at 37°C for an additional minute.
- When your cells are dislodged, move your flask back into the tissue culture hood and add 3 mL of PBS.
- To ensure you collect all of the cells in your flask, pipet the PBS down the bottom of the flask to wash the cells from the surface.
- Repeat this a total of 3 times.
- Note: do not take up or release all the liquid, in order to avoid bubbles.
- Transfer the suspended cells into a labeled 15 mL conical tube.
- Centrifuge your suspensions at 500 rpm for 10 min to pellet the cells.
- Carefully remove your tubes from the centrifuge and return to your bench in the main laboratory.
- Avoid agitating your tubes as the pellet is easily disrupted.
- Slowly pour the supernatent from your tubes into your 50 mL waste conical tube.
- Do not shake, tap, or flick the tubes to remove excess liquid as this will disrupt your cell pellet.
- Add 350 μL of RLT and pipet up and down to mix.
- Transfer the cell / RLT suspension to a Qiashredder column (color??).
- Be sure to label both the column insert and collection tube.
- Only 700 μL at a time can be loaded onto the column. If you have more than 700 μL, consult the teaching faculty.
- Centrifuge at 16,000 rpm for 2 min.
- Remove the columns from the collection tubes and add 700 μL of 70% ethanol, then pipet to mix.
- Transfer 700 μL of the RNA / ethanol suspension to an RNAeasy column (color??).
- Centrifuge at 8,000 rpm for 30 sec then discard the flow-through from the collection tube in your 50 mL waste conical tube.
- Repeat Steps #17 - 18 until all of the RNA / ethanol suspension has been passed through the RNAeasy column.
- Add 700 μL of RW1 and centrifuge at 8,000 rpm for 30 sec, then discard the flow-through in your 50 mL waste conical tube.
- Add 500 μL of RPE and centrifuge at 8,000 rpm for 30 sec, then discard the flow-through in your 50 mL waste conical tube.
- Add 500 μL of RPE and centrifuge at 8,000 rpm for 2 min, then discard the flow-through in your 50 mL waste conical tube.
- Move the columns into new collection tubes, then centrifuge at 16,000 rpm for 1 min.
- Move the columns into 1.5 mL tubes.
- Remove the caps from the tubes by cutting them off with scissor as they can break off in the centrifuge.
- Label the base of the tubes to ensure you keep track of your samples.
- Add 30 μL of RNase free water, then centrifuge at 8,000 rpm for 1 min.
- Alert the teaching faculty when you are done and you will be escorted to the nanodrop to check the concentrations of your purified RNA samples.
Part 2b: Generate cDNA
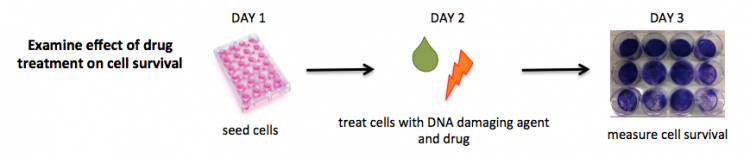
Part 3: Complete cell survival assay
Today you will complete the cell survival assay. As discussed previously, you will use crystal violet staining as a readout for cell abundance. While working with crystal violet is important that you wear gloves and a lab coat as it is carcinogenic and will permanently stain your clothing. It is also important that all crystal violet waste is collected in the appropriate waste containers and not poured in the sinks.
- Retrieve your 12-well plate from the 37 °C incubator in the tissue culture room and and visually inspect your cells with a microscope.
- Record your observations concerning media color, confluency, etc. in your laboratory notebook.
- Carefully carry your plate to your bench in the main laboratory.
- Aspirate the spent media from each well.
- Be sure to attach a yellow pipet tip to the Pasteur pipet on the aspirator before using.
- Change the yellow pipet between wells so as not to cross-contaminate.
- Add ~2 mL of PBS to each well and gently rock the plate back and forth to wash the cells.
- Aspirate the PBS from each well.
- Again, change the yellow pipet tip to avoid cross-contamination.
- Add 200 μL of 0.2% crystal violet dye solution to each well.
- Carefully move your plate to the rocking table and incubate for 30 min.
- Retrieve your plate and add 1 mL of dH2 to each well.
- Add the dH2 to the crystal violet by slowly pipeting it down the side of the well rather than 'blasting' it directly into the well.
- To remove the crystal violet / dH2 from your plate, flip the plate upside down over a waste container.
- Repeat Steps #8 - 9 a total of 3 times.
- If the waste dH2 from the final wash is still dark purple, consult the teaching faculty about performing additional washes.
- Add 1 mL of 1% SDS to each well and incubate your plate on your benchtop for 30 min.
- Prepare your samples for absorbance measurements using the spectrophotometer.
- Gather 12 cuvettes from the front laboratory bench and add 900 μL of 1% SDS to each.
- It may be helpful to label the 'rough' side of your cuvettes to keep track of your samples.
- Transfer 100 μL from each well into a cuvette.
- You may need to pipet the contents of the well to homogenize cell / dye clumps.
- To mix the liquid in your cuvette, cover the top of the cuvette with your gloved thumb and shake up and down.
- Measure and record the A570 for each of your samples, then post the data to the wiki.
- Pour the contents of your cuvettes into the crystal violet waste container and dispose of them in your benchtop waste bucket.
Reagents
Next day: Examine transcript levels in response to DNA damage
Previous day: Complete Western blot and induce DNA damage for survival and quantitative PCR assays