Difference between revisions of "Assignment 6, Part 2: electronics written problems"
From Course Wiki
Juliesutton (Talk | contribs) (Created page with "__NOTOC__ This is Part 2 of Assignment 6. <br /> ==Ideal elements== {{Template:Assignment Turn In|messa...") |
|||
| (2 intermediate revisions by one user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | {{Template:20.309}} | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
| − | This is Part 2 of [[ | + | This is Part 2 of [[Assignment 6 Overview: two color microscope| Assignment 6]]. |
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| Line 36: | Line 37: | ||
For each of the circuits in the previous problem, find two equivalent circuits — the first one consisting of a single ''voltage'' source and a single resistor, and the second one consisting of one ''current'' source and one resistor. In both equivalent circuits, the I-V curve at the V<sub>out</sub> the port should be identical to the original circuit. | For each of the circuits in the previous problem, find two equivalent circuits — the first one consisting of a single ''voltage'' source and a single resistor, and the second one consisting of one ''current'' source and one resistor. In both equivalent circuits, the I-V curve at the V<sub>out</sub> the port should be identical to the original circuit. | ||
}} | }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{Template:Assignment 6 navigation}} | ||
| + | {{Template:20.309 bottom}} | ||
Latest revision as of 05:20, 5 April 2020
This is Part 2 of Assignment 6.
Ideal elements
Resistive circuits
| |
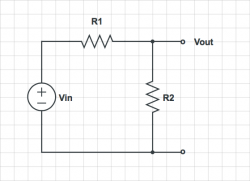
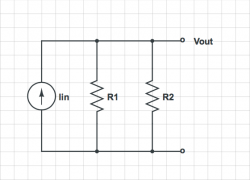
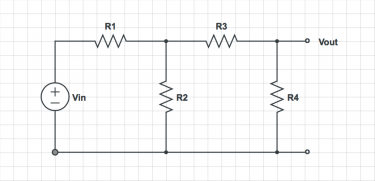
For each of the circuits below, find the voltage at each node and the current through each element. |
| 1 | 2 |
|---|---|
|
|
| 3 | |
| |
Equivalent circuits
- Overview
- Part 1: two-color microscope
- Part 2: circuit problems
Back to 20.309 Main Page.