Difference between revisions of "20.109(S14):Transcript-level analysis (Day6)"
MAXINE JONAS (Talk | contribs) m (8 revisions: Transfer 20.109(S14) to HostGator) |
|||
| (6 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
| − | + | As you have seen in 20.109 and in the scientific literature, imaging technologies can provide valuable insight into biological systems. Each different imaging method has a particular set of associated advantages and drawbacks. For example, fluorescence microscopy can provide high-resolution images, but the penetration depth at which samples can be viewed is limited (though improved by recent developments such as multiphoton microscopy). Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) has just the opposite characteristics, and its potential for large-area and deep tissue imaging makes it quite useful in medicine. | |
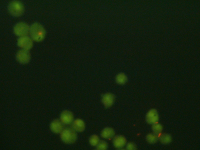
| − | + | [[Image:20.109_CTE_image-basis.png|thumb|200px|'''Sample image of live cells for analysis''']] | |
| + | [[Image:20.109_CTE_analysis-ex.png|thumb|200px|'''Sample cell counting result for image above''']] | ||
| − | + | Whatever the imaging modality, the resulting plethora of imaging information, especially if at the single-cell level or through multiple sections of a 3D-tissue, requires potent and efficient analysis tools. Many image analysis software packages are commercially available, with varying degrees of user-friendliness, algorithm efficiency, etc. Today, you’ll use an open source analysis package from NIH called [http://rsb.info.nih.gov/ij/ ImageJ]. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | Basic image processing includes noise reduction, enhancement of brightness and contrast, thresholding images based on intensity (e.g., everything below a certain intensity value is considered background), and colorizing. For cells, typical analyses include measurement of surface area (i.e., how spread is the cell morphology?), tracking individual cell intensities (these may reflect intracellular flux of calcium or other molecules of interest), and counting cell populations. In general, analyses that require tracking cells over time are more complicated than static analyses. For example, tracking cell migration typically involves setting thresholds with respect to both intensity and size, then running an algorithm that calculates the centroid of each cell at each time-point and from those centroids the cell’s path and velocity. Fully automated tracking can be challenged by cells dropping in and out of the plane of view, crossing paths with other similar-looking cells, or just moving very quickly. On the other hand, fully manual tracking – which utilizes the power the human eye to avoid mistracking cells – is tedious and time-consuming, not to mention that it will still have a non-zero error rate. Thankfully, your focus today will be on static measurements! | |
| − | + | Now, let’s return to thinking about the structure of cartilage for a bit. Our work in this module so far has focused on on the cells themselves (viability and morphology) and on the ECM protein collagen. While collagen makes up ~50-60% of the dry weight of cartilage tissue, another key feature is a high proteoglycan content of ~ 15-30%. Proteoglycans are proteins carrying glycosaminoglycan (GAG) chains, which commonly include keratan and chondroitin sulfates. Aggrecan is the major proteoglycan in cartilage tissue, and many aggrecan monomers attach to a single hyaluronic acid chain to form large aggregates – hence the name. The many negative side chains of proteoglycans (primarily sulfates and carboxylic acids) repel each other, and contribute to the osmotic swelling properties of cartilage tissue. Proteoglycans are trapped within the collagen matrix, the former being primarily responsible for compressive strength (due to changes in osmotic swelling) and the latter for tensile strength. Proteoglycans also contribute to joint lubrication and response to shearing forces. | |
| + | |||
| + | Osteoarthritis, the primary disease that cartilage tissue engineering aims to treat, is associated with a loss of proteoglycan content. This loss in turn reduces the swelling and elasticity of cartilage tissue, and its ability to respond to compressive loads. This leads to collagen degradation, joint inflammation, and cartilage tissue destruction. Thus, a physiological proteoglycan content is essential for an engineered cartilage tissue. Today we will measure proteoglycan production in your samples by using 1,9-dimethylmethylene blue (DMMB). DMMB is cationic dye that thus readily binds to the negatively charged moieties on proteoglycans; its absorbance spectrum changes when complexed with the GAG chains. However, at the usual pH of the assay (pH 3) DMMB as readily binds the carboxyl groups on alginate as it does the (primarily) sulfate groups on proteoglycans produced by healthy chondrocytes. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8954546 Enobakhare and colleagues] reasoned that at an even lower pH (pH 1.5, as it turns out) the sulfate groups could be selectively bound while the carboxyl groups became protonated and thus uncharged. Because you cultured your cells in alginate, we will perform this modified DMMB assay today. | ||
==Protocols== | ==Protocols== | ||
| − | ===Part 1: | + | ===Part 1: Day 2 of ELISA=== |
| − | + | #Begin by washing your samples. (Check the protocol on Day 5 for a refresher.) This time do four washes instead of only two – you don’t want to amplify the signal from any primary antibody that isn’t firmly bound to your samples. | |
| + | #When you are ready, ask the teaching faculty for some alkaline-phosphatase labeled secondary antibody (this should be diluted at the last minute). Add 100 μL of diluted antibody per well. Incubate for 90 min (at room temperature), and work on Parts 2 and 3 of today's protocol. | ||
| + | #Your final wash step should be very thorough because it again precedes an amplification step. To reduce non-specific binding and improve your signal-to-noise ratio, do four careful washes. In the next step, we are adding the substrate for the alkaline phosphatase enzyme. | ||
| + | #Ask the teaching faculty for development buffer and a pNPP (p-nitrophenyl phosphate) pellet. Vortex until the pellet is fully dissolved in the buffer, and then add 100 μL of development solution to each well. Cover your plate with aluminum foil now! | ||
| + | #Every few minutes, check if the samples are becoming yellow. This change will most likely take place between 10-30 minutes for each plate. | ||
| + | #*The top 1-3 samples in the standards may become bright yellow, while the bottom 1-2 samples may appear very pale yellow. Once again, we have a signal:noise issue. If you wait too long, more samples will become saturated (bright), and the results will be meaningless. If you don’t wait long enough, you may miss a positive but low result. | ||
| + | #*Use your best judgment! Ideally, look for a couple of your samples (not just the standards) to have developed some color. However, note that some samples simply may not have measurable protein content. Feel free to ask the teaching faculty for advice. | ||
| + | #When your samples are ready, add 100 μL of Stop Solution (0.4 M NaOH). A member of the teaching faculty will take the plates to BPEC and read them in the absorbance plate reader at 420 nm. | ||
| + | #You can hang around and analyze your data today (see [[20.109%28S13%29:Protein-level_and_wrap-up_analysis_%28Day7%29#Part_1:_ELISA_analysis | Part 1]] of the Day 7 protocol), or wait until next time. | ||
| − | + | ===Part 2: Proteoglycan assay=== | |
| − | + | The colorimetric response to the formation of DMMB-GAG complexes is short-lived, and thus the absorbances must be measured within 5 minutes of combining the dye and samples. Tell the teaching faculty when you plan to do the assay. With their go ahead, add the standards and samples to the plate. Then, you will go upstairs to the BPEC facility with an instructor and add the dye then and there. | |
| − | + | #You will be given chondroitin sulfate (CS) at 200 μg/mL. Prepare doubling dilutions of this GAG in water that contains 0.15 % alginate such that you will have 100 μL of each dilution left over for distribution. | |
| + | #*You will only need 80 μL as you can see below, but should always prepare some excess to account for pipetting error. | ||
| + | #*Alginate is included in order to account for any slight background response that it may still have at pH 1.5. | ||
| + | #Add 40 μL duplicate samples of CS to columns 1 and 2 of your plate, in all eight rows A-H. | ||
| + | #In column 3, add duplicates of your first culture sample (A-B) followed by duplicates of your second culture sample (C-D), just as you did for the ELISA assay. | ||
| + | #In rows E-H of column 3, add 40 μL plain water/alginate. | ||
| + | #When you are ready, you will go to BPEC with an instructor. There, add 250 μL of DMMB to each well and immediately measure the A<sub>595</sub> using the plate reader. | ||
| + | #*The detection limit of this assay appears to be on the order of 10 μg/mL before dilution (or about 1.3 μg/mL overall). | ||
| + | #You can try putting the average blank value in your standard curve as the 0 concentration point. However, you should not do a blank subtraction, as the blank is of course the highest value. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Part 3: qPCR analysis=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Your qPCR analysis will be based on the paper by Michael Pfaffl [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11328886 (link to abstract here)]. Equation 1 in the paper defines a relative gene expression ratio. You will calculate change in expression for two targets, collagen I and collagen II. The reference ("ref") RNA is the 18S rRNA gene in both cases. The crossing point ("CP") values were calculated from the samples that you ran last time and can be downloaded from today's [[Talk:20.109%28S14%29:Transcript-level_analysis_%28Day6%29 | '''Talk''']] page. The amplification efficiency ("E") values for each primer set were calculated from pilot experiments using a cDNA dilution series, giving data similar to that in Figure 1 of the Pfaffl paper. The E values are 1.924, 1.888, and 1.776 for CN II, CN I, and 18S, respectively. | ||
| + | |||
| + | #On today's Talk page you will download your CP (also called C<sub>T</sub>) values. You will also be able to view section-wide melt curves and amplification curves per each primer set. | ||
| + | #Begin by looking at the CP values (and raw or threshold-processed curves if available). Comment on replicate agreement. | ||
| + | #*Be sure to also read any additional notes associated with your sample (in the same file below the Cp value list). These note any samples that registered as having no signal to the machine or which had an odd shape and may represent an artifact or be less trustworthy than the associated duplicate. | ||
| + | #Calculate the average and standard deviation of each of your 6 pairs of CP values. | ||
| + | #Based on your average CP values, calculate the change in gene expression if you consider one of your samples the control and the other the sample. '''You might want to start with the practice calculation in step 6.''' | ||
| + | #*For multi-group collaborations, you can consistently use one of the 4<sup>+</sup> samples as the control if appropriate. | ||
| + | #*Note that the sample is subtracted ''from'' the control (to ultimately get the expression ratio of the sample relative to the control), not the other way around. | ||
| + | #You can also try to calculate the gene expression change relative to pure chondrocytes or pure stem cells shortly after cell isolation. However, to give reliable results these samples should have been run in the same plate as yours with the same day's master mix, so take any comparisons with a huge grain of salt. The CP values are listed in the table below. | ||
| + | #*Note that the stem cell CN II value may be somewhat off, due to combining two imperfect experiments. It may be closer to 22, or even a bit higher. (Which makes a big difference to the ratio!) | ||
| + | #CP values for extended (2D) chondrocyte culture in medium with or without both proline and ascorbate are also shown in the table below. As practice and a check on your ratio calculations above, you should try calculating the expression ratios for with vs. without chondrocytic media factors, with vs. pure chondrocytes, without vs. pure chondrocytes, and pure chondrocytes vs. pure stem cells (where "pure" means a freshly isolated population). You can compare your answers to those in the table, and fix your analysis above if needed. | ||
| + | #*You can see that in 2D culture, the additions of proline and ascorbate make only a small impact, if any, on CN II and CN I expression. | ||
| + | #Finally, look briefly at your melt curves and any additional notes in the file from step 2. As we discussed in lecture, the samples should each exhibit a single peak that can be attributed to the melting of the desired product. There may also be a small primer-dimer peak, about 10% of the main peak intensity. Do any of your samples have a substantial amount of non-specific (most likely primer-dimer) product? | ||
| + | <br style="clear:both;"/> | ||
| + | <center> | ||
| + | {| border="1" | ||
| + | |Sample | ||
| + | | CN I CP | ||
| + | | CN II CP | ||
| + | | 18S CP | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |chondrocytes | ||
| + | | 22.3 | ||
| + | | 14 | ||
| + | |13.5 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |2D culture with factors | ||
| + | |15.8 | ||
| + | |12.9 | ||
| + | |10.7 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |2D culture no proline, asc | ||
| + | |16.7 | ||
| + | |14.5 | ||
| + | |11.9 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |stem cells | ||
| + | |17.2 | ||
| + | |19.6 | ||
| + | |11.1 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br style="clear:both;"/> | ||
| + | {| border="1" | ||
| + | |Control | ||
| + | |Sample | ||
| + | |CN II relative expression ratio | ||
| + | |CN I relative expression ratio | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |No proline, ascorbate | ||
| + | |With factors | ||
| + | |1.4 | ||
| + | |0.89 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Chondrocytes | ||
| + | |No proline, ascorbate | ||
| + | |0.29 | ||
| + | |14 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Chondrocytes | ||
| + | |With factors | ||
| + | |0.41 | ||
| + | |12(.5) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Stem cells | ||
| + | |Chondrocytes | ||
| + | |15(5) | ||
| + | |0.16 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | </center> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Part 4: Cross-group research idea discussion=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | You can complete this discussion today or outside of class, according to the pairings on today's [[Talk:20.109%28S14%29:Transcript-level_analysis_%28Day6%29 | Talk]] page. | ||
| + | |||
| + | You should be on your way to becoming an expert on your research topic. You should have been reading and thinking a lot about it and you may feel <br> | ||
| + | (a) like there's too much to read <br> | ||
| + | (b) like you have too many ideas and no way to map or prioritize them <br> | ||
| + | (c) like you don't understand what you're reading <br> | ||
| + | (d) all of the above. <br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | One of the best ways to help frame the problem for yourself is to discuss it with someone new. Take some time today to talk with someone from '''another''' lab group. That group will offer you a fresh ear to consider your proposal. Try to describe your research problem to them. Articulate why it's important. Tell them about some recent, relevant data. Describe what you're proposing to do and what the findings from your experiments might reveal. Throughout your discussion, keep careful track of the questions they ask since these will point you to the confusing concepts or fuzzy parts of your explanation or understanding. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Then be a good listener to hear the proposal that they've been working on. Ask lots of questions. No questions are dumb. You are there to offer a naive ear and seek complete explanations. Next time you meet with your partner you can share how your cross-group discussions went. Try to identify repeated questions or concerns since these are probably the holes in the project as it stands. You can rework your proposal based on the conversations you've had. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Part 5: Continue ImageJ analysis (optional)=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Work on your live/dead assay imaging analysis if you did not do so last time. | ||
==For next time== | ==For next time== | ||
| − | + | 1. Your [[20.109%28S13%29:_Cell-biomaterial_engineering_report |Module 3 report]] will be due before you leave lab next time. Continue working on it.<br> | |
| + | 2. Based on the feedback that you got from your peers and/or the teaching faculty today, continue to define your research proposal and update your wiki page with your partner. You do not need to hand anything in, but keep in mind that your talk is one week from today. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Reagent List== | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Goat anti-rabbit antibody conjugated to alkaline phosphatase (AP) | ||
| + | ** from Bio-Rad | ||
| + | ** used at 1:1000 in block buffer (see Day 5 for recipe) | ||
| + | *Bio-rad AP substrate kit | ||
| + | ** development buffer | ||
| + | ** p-nitrophenyl phosphate tablets | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Chemicals for PG assay from Sigma Aldrich | ||
| + | **aqueous 50 μM DMMB with 0.2% sodium formate and 0.5% ethanol, to pH 1.5 with formic acid | ||
| + | **chondroitin 6-sulfate | ||
==Navigation Links== | ==Navigation Links== | ||
| − | Next Day: [ | + | Next Day: [[20.109(S14):Protein-level and wrap-up analysis (Day7)| Protein-level and wrap-up analysis]] |
| − | Previous Day: [ | + | Previous Day: [[20.109(S14):Initiating transcript and protein assays (Day5)| Initiating transcript and protein assays]] |
Latest revision as of 13:59, 29 July 2015
Contents
Introduction
As you have seen in 20.109 and in the scientific literature, imaging technologies can provide valuable insight into biological systems. Each different imaging method has a particular set of associated advantages and drawbacks. For example, fluorescence microscopy can provide high-resolution images, but the penetration depth at which samples can be viewed is limited (though improved by recent developments such as multiphoton microscopy). Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) has just the opposite characteristics, and its potential for large-area and deep tissue imaging makes it quite useful in medicine.
Whatever the imaging modality, the resulting plethora of imaging information, especially if at the single-cell level or through multiple sections of a 3D-tissue, requires potent and efficient analysis tools. Many image analysis software packages are commercially available, with varying degrees of user-friendliness, algorithm efficiency, etc. Today, you’ll use an open source analysis package from NIH called ImageJ.
Basic image processing includes noise reduction, enhancement of brightness and contrast, thresholding images based on intensity (e.g., everything below a certain intensity value is considered background), and colorizing. For cells, typical analyses include measurement of surface area (i.e., how spread is the cell morphology?), tracking individual cell intensities (these may reflect intracellular flux of calcium or other molecules of interest), and counting cell populations. In general, analyses that require tracking cells over time are more complicated than static analyses. For example, tracking cell migration typically involves setting thresholds with respect to both intensity and size, then running an algorithm that calculates the centroid of each cell at each time-point and from those centroids the cell’s path and velocity. Fully automated tracking can be challenged by cells dropping in and out of the plane of view, crossing paths with other similar-looking cells, or just moving very quickly. On the other hand, fully manual tracking – which utilizes the power the human eye to avoid mistracking cells – is tedious and time-consuming, not to mention that it will still have a non-zero error rate. Thankfully, your focus today will be on static measurements!
Now, let’s return to thinking about the structure of cartilage for a bit. Our work in this module so far has focused on on the cells themselves (viability and morphology) and on the ECM protein collagen. While collagen makes up ~50-60% of the dry weight of cartilage tissue, another key feature is a high proteoglycan content of ~ 15-30%. Proteoglycans are proteins carrying glycosaminoglycan (GAG) chains, which commonly include keratan and chondroitin sulfates. Aggrecan is the major proteoglycan in cartilage tissue, and many aggrecan monomers attach to a single hyaluronic acid chain to form large aggregates – hence the name. The many negative side chains of proteoglycans (primarily sulfates and carboxylic acids) repel each other, and contribute to the osmotic swelling properties of cartilage tissue. Proteoglycans are trapped within the collagen matrix, the former being primarily responsible for compressive strength (due to changes in osmotic swelling) and the latter for tensile strength. Proteoglycans also contribute to joint lubrication and response to shearing forces.
Osteoarthritis, the primary disease that cartilage tissue engineering aims to treat, is associated with a loss of proteoglycan content. This loss in turn reduces the swelling and elasticity of cartilage tissue, and its ability to respond to compressive loads. This leads to collagen degradation, joint inflammation, and cartilage tissue destruction. Thus, a physiological proteoglycan content is essential for an engineered cartilage tissue. Today we will measure proteoglycan production in your samples by using 1,9-dimethylmethylene blue (DMMB). DMMB is cationic dye that thus readily binds to the negatively charged moieties on proteoglycans; its absorbance spectrum changes when complexed with the GAG chains. However, at the usual pH of the assay (pH 3) DMMB as readily binds the carboxyl groups on alginate as it does the (primarily) sulfate groups on proteoglycans produced by healthy chondrocytes. Enobakhare and colleagues reasoned that at an even lower pH (pH 1.5, as it turns out) the sulfate groups could be selectively bound while the carboxyl groups became protonated and thus uncharged. Because you cultured your cells in alginate, we will perform this modified DMMB assay today.
Protocols
Part 1: Day 2 of ELISA
- Begin by washing your samples. (Check the protocol on Day 5 for a refresher.) This time do four washes instead of only two – you don’t want to amplify the signal from any primary antibody that isn’t firmly bound to your samples.
- When you are ready, ask the teaching faculty for some alkaline-phosphatase labeled secondary antibody (this should be diluted at the last minute). Add 100 μL of diluted antibody per well. Incubate for 90 min (at room temperature), and work on Parts 2 and 3 of today's protocol.
- Your final wash step should be very thorough because it again precedes an amplification step. To reduce non-specific binding and improve your signal-to-noise ratio, do four careful washes. In the next step, we are adding the substrate for the alkaline phosphatase enzyme.
- Ask the teaching faculty for development buffer and a pNPP (p-nitrophenyl phosphate) pellet. Vortex until the pellet is fully dissolved in the buffer, and then add 100 μL of development solution to each well. Cover your plate with aluminum foil now!
- Every few minutes, check if the samples are becoming yellow. This change will most likely take place between 10-30 minutes for each plate.
- The top 1-3 samples in the standards may become bright yellow, while the bottom 1-2 samples may appear very pale yellow. Once again, we have a signal:noise issue. If you wait too long, more samples will become saturated (bright), and the results will be meaningless. If you don’t wait long enough, you may miss a positive but low result.
- Use your best judgment! Ideally, look for a couple of your samples (not just the standards) to have developed some color. However, note that some samples simply may not have measurable protein content. Feel free to ask the teaching faculty for advice.
- When your samples are ready, add 100 μL of Stop Solution (0.4 M NaOH). A member of the teaching faculty will take the plates to BPEC and read them in the absorbance plate reader at 420 nm.
- You can hang around and analyze your data today (see Part 1 of the Day 7 protocol), or wait until next time.
Part 2: Proteoglycan assay
The colorimetric response to the formation of DMMB-GAG complexes is short-lived, and thus the absorbances must be measured within 5 minutes of combining the dye and samples. Tell the teaching faculty when you plan to do the assay. With their go ahead, add the standards and samples to the plate. Then, you will go upstairs to the BPEC facility with an instructor and add the dye then and there.
- You will be given chondroitin sulfate (CS) at 200 μg/mL. Prepare doubling dilutions of this GAG in water that contains 0.15 % alginate such that you will have 100 μL of each dilution left over for distribution.
- You will only need 80 μL as you can see below, but should always prepare some excess to account for pipetting error.
- Alginate is included in order to account for any slight background response that it may still have at pH 1.5.
- Add 40 μL duplicate samples of CS to columns 1 and 2 of your plate, in all eight rows A-H.
- In column 3, add duplicates of your first culture sample (A-B) followed by duplicates of your second culture sample (C-D), just as you did for the ELISA assay.
- In rows E-H of column 3, add 40 μL plain water/alginate.
- When you are ready, you will go to BPEC with an instructor. There, add 250 μL of DMMB to each well and immediately measure the A595 using the plate reader.
- The detection limit of this assay appears to be on the order of 10 μg/mL before dilution (or about 1.3 μg/mL overall).
- You can try putting the average blank value in your standard curve as the 0 concentration point. However, you should not do a blank subtraction, as the blank is of course the highest value.
Part 3: qPCR analysis
Your qPCR analysis will be based on the paper by Michael Pfaffl (link to abstract here). Equation 1 in the paper defines a relative gene expression ratio. You will calculate change in expression for two targets, collagen I and collagen II. The reference ("ref") RNA is the 18S rRNA gene in both cases. The crossing point ("CP") values were calculated from the samples that you ran last time and can be downloaded from today's Talk page. The amplification efficiency ("E") values for each primer set were calculated from pilot experiments using a cDNA dilution series, giving data similar to that in Figure 1 of the Pfaffl paper. The E values are 1.924, 1.888, and 1.776 for CN II, CN I, and 18S, respectively.
- On today's Talk page you will download your CP (also called CT) values. You will also be able to view section-wide melt curves and amplification curves per each primer set.
- Begin by looking at the CP values (and raw or threshold-processed curves if available). Comment on replicate agreement.
- Be sure to also read any additional notes associated with your sample (in the same file below the Cp value list). These note any samples that registered as having no signal to the machine or which had an odd shape and may represent an artifact or be less trustworthy than the associated duplicate.
- Calculate the average and standard deviation of each of your 6 pairs of CP values.
- Based on your average CP values, calculate the change in gene expression if you consider one of your samples the control and the other the sample. You might want to start with the practice calculation in step 6.
- For multi-group collaborations, you can consistently use one of the 4+ samples as the control if appropriate.
- Note that the sample is subtracted from the control (to ultimately get the expression ratio of the sample relative to the control), not the other way around.
- You can also try to calculate the gene expression change relative to pure chondrocytes or pure stem cells shortly after cell isolation. However, to give reliable results these samples should have been run in the same plate as yours with the same day's master mix, so take any comparisons with a huge grain of salt. The CP values are listed in the table below.
- Note that the stem cell CN II value may be somewhat off, due to combining two imperfect experiments. It may be closer to 22, or even a bit higher. (Which makes a big difference to the ratio!)
- CP values for extended (2D) chondrocyte culture in medium with or without both proline and ascorbate are also shown in the table below. As practice and a check on your ratio calculations above, you should try calculating the expression ratios for with vs. without chondrocytic media factors, with vs. pure chondrocytes, without vs. pure chondrocytes, and pure chondrocytes vs. pure stem cells (where "pure" means a freshly isolated population). You can compare your answers to those in the table, and fix your analysis above if needed.
- You can see that in 2D culture, the additions of proline and ascorbate make only a small impact, if any, on CN II and CN I expression.
- Finally, look briefly at your melt curves and any additional notes in the file from step 2. As we discussed in lecture, the samples should each exhibit a single peak that can be attributed to the melting of the desired product. There may also be a small primer-dimer peak, about 10% of the main peak intensity. Do any of your samples have a substantial amount of non-specific (most likely primer-dimer) product?
| Sample | CN I CP | CN II CP | 18S CP |
| chondrocytes | 22.3 | 14 | 13.5 |
| 2D culture with factors | 15.8 | 12.9 | 10.7 |
| 2D culture no proline, asc | 16.7 | 14.5 | 11.9 |
| stem cells | 17.2 | 19.6 | 11.1 |
| Control | Sample | CN II relative expression ratio | CN I relative expression ratio |
| No proline, ascorbate | With factors | 1.4 | 0.89 |
| Chondrocytes | No proline, ascorbate | 0.29 | 14 |
| Chondrocytes | With factors | 0.41 | 12(.5) |
| Stem cells | Chondrocytes | 15(5) | 0.16 |
Part 4: Cross-group research idea discussion
You can complete this discussion today or outside of class, according to the pairings on today's Talk page.
You should be on your way to becoming an expert on your research topic. You should have been reading and thinking a lot about it and you may feel
(a) like there's too much to read
(b) like you have too many ideas and no way to map or prioritize them
(c) like you don't understand what you're reading
(d) all of the above.
One of the best ways to help frame the problem for yourself is to discuss it with someone new. Take some time today to talk with someone from another lab group. That group will offer you a fresh ear to consider your proposal. Try to describe your research problem to them. Articulate why it's important. Tell them about some recent, relevant data. Describe what you're proposing to do and what the findings from your experiments might reveal. Throughout your discussion, keep careful track of the questions they ask since these will point you to the confusing concepts or fuzzy parts of your explanation or understanding.
Then be a good listener to hear the proposal that they've been working on. Ask lots of questions. No questions are dumb. You are there to offer a naive ear and seek complete explanations. Next time you meet with your partner you can share how your cross-group discussions went. Try to identify repeated questions or concerns since these are probably the holes in the project as it stands. You can rework your proposal based on the conversations you've had.
Part 5: Continue ImageJ analysis (optional)
Work on your live/dead assay imaging analysis if you did not do so last time.
For next time
1. Your Module 3 report will be due before you leave lab next time. Continue working on it.
2. Based on the feedback that you got from your peers and/or the teaching faculty today, continue to define your research proposal and update your wiki page with your partner. You do not need to hand anything in, but keep in mind that your talk is one week from today.
Reagent List
- Goat anti-rabbit antibody conjugated to alkaline phosphatase (AP)
- from Bio-Rad
- used at 1:1000 in block buffer (see Day 5 for recipe)
- Bio-rad AP substrate kit
- development buffer
- p-nitrophenyl phosphate tablets
- Chemicals for PG assay from Sigma Aldrich
- aqueous 50 μM DMMB with 0.2% sodium formate and 0.5% ethanol, to pH 1.5 with formic acid
- chondroitin 6-sulfate
Next Day: Protein-level and wrap-up analysis
Previous Day: Initiating transcript and protein assays