Nonlinear regression
… the safe use of regression requires a good deal of thought and a good dose of skepticism
Review of linear regression
Linear Regression is a method for finding the magnitude of the relationship between two variables that co-vary. The technique assumes that a straight line characterizes the relationship between the two quantities: 𝑦=𝛽𝑥+𝛼, where 𝛽 is the true slope and 𝛼 is the true intercept. Some examples of physical systems that are modeled well by lines include resistors (V=IR) and springs (F=kx).
A simple way to find α and β is to measure the y at two different values of x, giving the datapoints (xi, yi); i = {1,2}. If the two points are precisely known, solving for the exact values of 𝛼 and 𝛽 is trivial. Unfortunately, all physical measurements include noise. The presence of noise precludes finding the exact values of 𝛼 and 𝛽.
Measurement noise can be modeled by adding a noise term, εi, to the right side of the model equation: yi=Βix+α+εix. The function of linear regression is to produce estimates of 𝛼 and 𝛽, denoted by α̂ and β̂, from a sample of N value pairs (xi, yi); i = {1, ..., N} that includes noise in the y-values. The most common regression model assumes that x is known exactly. In practice, regression works well if the relative magnitude of noise in x is much smaller than y.
The most common type of LR minimizes the value of the squared vertical distances between observed and predicted values
Model :
Assumptions:
the independent variable 𝑥 is known with certainty (or at least very much less error than 𝑦)
𝜀 is an independent, random variable with 𝜇=0
The distribution of 𝜀 is symmetric around the origin
the likelihood of large errors is less than small ones
Uncertainty in slope estimate
The error in slope 𝑊=𝛽 ̂−𝛽
Variance of 𝑊 characterizes slope error
You can calculate a 95% (or other significance level) confidence interval for 𝛽 ̂
What factors should the uncertainty depend on?
Estimate 𝜎^2 (𝑊): 𝑉^2 (𝑊)=(∑▒〖𝑟_𝑖^ 〗^2 )/((𝑁−2)∑▒〖(𝑥_𝑖−𝑥 ̅)〗^2 )
N-2 is a “penalty” because regression line minimizes variance of residuals
If the interval contains 0, the null hypothesis that 𝛽=0 cannot be rejected
Step 1: PLOT THE DATA
Examine the residuals
- plot 'em for an informal look
- various tests of residuals exist
Overview of nonlinear regression
“If your program generates an error message rather than curve fitting results, you probably won’t be able to make sense of the exact wording of the message”
— Fitting Models to Biological Data using Linear and Nonlinar Regression by Motulsky and Shristopoulos
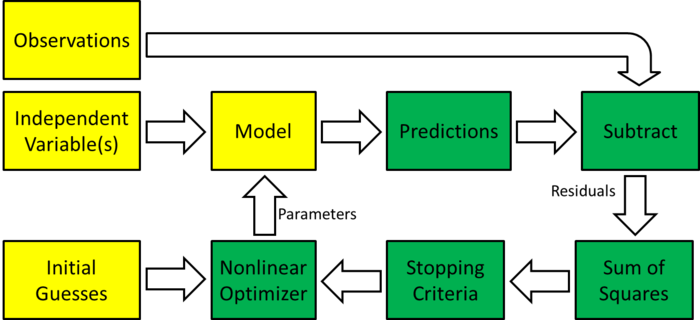
| Block diagram of nonlinear regression |