Difference between revisions of "DNA Melting: Simulating DNA Melting - Intermediate Topics"
Steven Nagle (Talk | contribs) m (moved Matlab:Simulating DNA Melting to DNA Melting Part 3: Simulating DNA Melting - Intermediate Topcs: re-org.) |
MAXINE JONAS (Talk | contribs) (→Lab manual sections) |
||
| (36 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:20.309]] |
[[Category:DNA Melting Lab]] | [[Category:DNA Melting Lab]] | ||
| − | + | {{Template:20.309}} | |
| + | [[Category:Matlab]] | ||
| − | ===Add some noise=== | + | ===Add some noise to the RTD signal=== |
| − | You will certainly notice noise on the signals you capture in the lab. | + | You will certainly notice noise on the signals you capture in the lab. Noise will be an ''extremely'' important (and annoying) factor in this experiment because the melting curves will be differentiated. Differentiation emphasizes noise. In order to ensure that your data analysis script effectively handles the noise you are likely to observe, simulated random and impulse noise will be added to the signals. |
To simulate noise, we can use Matlab's <tt>randn</tt> function, which generates normally distributed random numbers with unity standard deviation. The two arguments tell <tt>randn</tt> to create a vector of random samples with size 1xlength(V_RTD). | To simulate noise, we can use Matlab's <tt>randn</tt> function, which generates normally distributed random numbers with unity standard deviation. The two arguments tell <tt>randn</tt> to create a vector of random samples with size 1xlength(V_RTD). | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
| − | noise = 0.001 * randn(1,length(sim1.V_RTD)); % Create noise vector, standard deviation=1mV | + | noise = 0.001 * randn(1,length(sim1.V_RTD))'; % Create noise vector, standard deviation=1mV |
sim1.V_RTD = sim1.V_RTD + noise; % Add simulated noise to the voltage signal | sim1.V_RTD = sim1.V_RTD + noise; % Add simulated noise to the voltage signal | ||
| + | figure(8) | ||
plot(sim1.time, sim1.V_RTD, 'r'); | plot(sim1.time, sim1.V_RTD, 'r'); | ||
xlabel('Time (sec)'); | xlabel('Time (sec)'); | ||
| Line 18: | Line 20: | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| − | [[Image: | + | [[Image:RTDNoisyHeatCoolCurve.png|350px|Simulated RTD voltage plot]] |
| − | + | Revisit your code from [[DNA Melting: Simulating DNA Melting - Basics]] and using the approach above add noise to your RTD voltage signal, then explore the behavior of your code for different levels of noise. In particular, you can add differentiation of the curve from Figure 6 and discover the issues with attempts to differentiate that signal without additional processing. You will likely find that you first need to either sort or bin your temperature data so that the f vs T function can be differentiated. Then also run this data through your fit function and observe any difference in the fit statistics. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | You are also encouraged to add noise at additional frequencies that you think might be present in the lab, then attempt to filter that data in Matlab to test the effectiveness of the RTD voltage filter design that you built in the lab. To do this, generate the noise (perhaps 60 Hz, pink noise, possibly high frequency noise from switching in the overhead lights, or even noise on the earth ground that could be coming from equipment elsewhere in the building) and add it to the signal from Figure 8. Remember it is a long way to the earth from our lab. Next filter that signal using your transfer function and the matlab command lsim. Then again run this data through your fit function. | |
| − | === | + | ===Add some noise to the sample fluorescence signal=== |
| − | + | Now that we have added noise to the RTD voltage signal, the next step is to do the same for the fluorescence signal. | |
| − | + | The output range of the transimpedance amplifier depends on many factors, including: dsDNA quantity, illumination intensity, fluorophore efficiency, optical system gain, photodiode efficiency, and electronic amplifier gain. All of the factors except dsDNA concentration essentialy remain constant. Thus, the output of the transimpedance amplifier can be modeled by a single overall system gain factor times the dsDNA fraction. In addition, the amplifier output may be offset by a constant DC value, which is simple to model. (If the output of your apparatus drifts significantly over time, you will need to improve your implementation and methods to minimize this.) | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
The output range of the transimpedance amplifier over the course of an experimental run can vary depending on several factors, including the amplifier gain, optical system gain, etc... A typical setup might produce values between, say, 0.5 and 7.2 Volts. The simulation code generates two random numbers to set the range and minimum value of the data. Your data analysis script will have to normalize the amplifier output voltage to a fractional value between 0 and 1. (What assumptions will you make about dsDNA concentration to do the normalization?) | The output range of the transimpedance amplifier over the course of an experimental run can vary depending on several factors, including the amplifier gain, optical system gain, etc... A typical setup might produce values between, say, 0.5 and 7.2 Volts. The simulation code generates two random numbers to set the range and minimum value of the data. Your data analysis script will have to normalize the amplifier output voltage to a fractional value between 0 and 1. (What assumptions will you make about dsDNA concentration to do the normalization?) | ||
| − | In addition to Gaussian noise, the high gain amplifier sometimes produces impulse noise. This can be caused by small static discharges, for example when a charged person sits down in a chair in the lab. | + | In addition to white Gaussian noise <ref> [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/White_noise White noise]</ref> (including shot noise from the photodiode and Johnson noise in your feedback resistors), the high gain amplifier sometimes produces impulse noise. This can be caused by small static discharges, for example when a charged person sits down in a chair in the lab, or by machinery switching on or off somewhere else in the building. Each of these latter noise sources would generally show up on your ground reference, even when connected to the building earth ground, an often imperfect grounding source. Your goal is first to provide as much filtering as possible in your circuitry. However, these noise sources are difficult to completely eliminate, so it is a good idea to include some filtering in your data analysis script. |
<pre> | <pre> | ||
| Line 49: | Line 39: | ||
Minimum = 2 * rand() - 1; % Minimum between +/- 1 | Minimum = 2 * rand() - 1; % Minimum between +/- 1 | ||
sim1.V_f = Range * sim1.dsDnaFraction + Minimum; % Scale output | sim1.V_f = Range * sim1.dsDnaFraction + Minimum; % Scale output | ||
| − | noise = 0.01 * randn(1,length(sim1.V_f)); | + | noise = 0.01 * randn(1,length(sim1.V_f))'; % Random noise, standard deviation=10mV |
sim1.V_f = sim1.V_f + noise; % Add random noise | sim1.V_f = sim1.V_f + noise; % Add random noise | ||
| − | noise = rand(1,length(sim1.V_f)); | + | noise = rand(1,length(sim1.V_f))'; % Uniformly distributed random numbers |
ImpulseNoiseProbability = 1 ./ 75; % Probability of impulse noise | ImpulseNoiseProbability = 1 ./ 75; % Probability of impulse noise | ||
noise = 20 * (noise < ImpulseNoiseProbability) - 10; % Quantize impulse noise | noise = 20 * (noise < ImpulseNoiseProbability) - 10; % Quantize impulse noise | ||
| − | sim1. | + | sim1.V_fNoisy = max(sim1.V_f, noise); % Add in impulse noise |
| − | plot(sim1.time, sim1. | + | figure(9) |
| + | plot(sim1.time, sim1.V_fNoisy) | ||
title('Fluorescence Voltage vs. Time'); | title('Fluorescence Voltage vs. Time'); | ||
xlabel('Time (s)'); | xlabel('Time (s)'); | ||
ylabel('Fluorescence Voltage (V)'); | ylabel('Fluorescence Voltage (V)'); | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | [[Image:SimNoisyDNAFractionVsTime.png|350px|Simulated RTD voltage plot]] | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | As in the last section, revisit your code from DNA Melting: Simulating DNA Melting - Basics but this time add noise to your fluorescence voltage signal, then explore the behavior of your code for different levels of noise. Then again run this data through your fit function. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | Here too you are encouraged to add noise at additional frequencies that you think might be present in the lab. What could you do to minimize the effects of these noise sources? Think of solutions both at the hardware level and at the software level and model both of them. | ||
| − | + | ===Add photobleaching effects=== | |
| + | Each time a SYBR Green molecule is excited by a photon, there is a small chance that it will be destroyed and permanently lose its ability to fluoresce. The effect of photobleaching on the measured fluorescence intensity can be significant. To demonstrate this, a model for photobleaching may be added to the simulation. In the model, a small, fixed percentage of the fluorophores are mathematically destroyed each time sample. This can be implemented with a simple integration. The derivation of this model can be found [http://dl.dropbox.com/u/12957607/Bleaching%20Correction%20Derivation.pdf here]. | ||
| − | + | The model does not completely describe observations, so in the code below, we have also added an additional time-linear bleaching relationship that has helped to explain the observed behavior. The fraction of fluorophores destroyed per time sample is set by the variable <tt>bleachingCoefficient</tt>, while the coefficient for the linear case is <tt>bleachingConstant</tt>. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | The fraction of fluorophores destroyed per time sample is set by the variable <tt> | + | |
<pre> | <pre> | ||
| − | sim1. | + | sim1.filtV_f = medfilt1(sim1.V_fNoisy,15); % temporarily remove shot noise |
| − | sim1. | + | sim1.fluorescenceNorm = sim1.filtV_f / max(sim1.filtV_f); % normalize photo diode signal to dsDNA fraction |
| − | sim1. | + | sim1.bleachingCoefficient = 3e-5; % 1/s, estimated from previous experiments |
| + | sim1.bleachingConstant = 3e-4; % 1/s, estimated from previous experiments | ||
| + | sim1.bleachingCorrection = (1 - sim1.bleachingCoefficient ... | ||
| + | .* cumsum(1 .* sim1.fluorescenceNorm)) ... | ||
| + | .* (1 - sim1.bleachingConstant .* (0:(length(sim1.fluorescenceNorm)... | ||
| + | - 1))'); % calclation of bleaching correction by two methods, exponetial and linear | ||
| + | sim1.fluorescenceBleached = sim1.fluorescenceNorm ... | ||
| + | .* sim1.bleachingCorrection; | ||
| + | Range = 5 + 4 * rand(); % Range between 5 and 9 | ||
| + | Minimum = 2 * rand() - 1; % Minimum between +/- 1 | ||
| + | sim1.V_fScaled = Range * sim1.fluorescenceBleached + Minimum; % Scale output | ||
| + | noise = rand(1,length(sim1.V_fScaled))'; % Uniformly distributed random numbers | ||
| + | ImpulseNoiseProbability = 1 ./ 75; % Probability of impulse noise | ||
| + | noise = 20 * (noise < ImpulseNoiseProbability) - 10; % Quantize impulse noise | ||
| + | sim1.V_fBleached = max(sim1.V_fScaled, noise); % Add in impulse noise | ||
| − | + | figure(10) | |
| − | + | plot(sim1.time, sim1.V_fBleached) | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | plot(sim1.time, sim1. | + | |
title('Relative Fluorescence vs. Time with Bleaching'); | title('Relative Fluorescence vs. Time with Bleaching'); | ||
xlabel('Time (s)'); | xlabel('Time (s)'); | ||
| Line 110: | Line 90: | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| − | [[Image: | + | [[Image:SimNoisyBleachedDNAFractionVsTime.png|350px|Fluorescence vs. time with photobleaching]] |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ==References== | |
| + | <references /> | ||
| − | + | {{Template:20.309 bottom}} | |
| − | + | ||
Latest revision as of 21:46, 17 August 2017
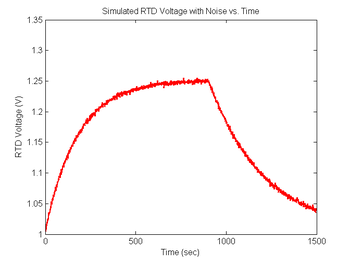
Add some noise to the RTD signal
You will certainly notice noise on the signals you capture in the lab. Noise will be an extremely important (and annoying) factor in this experiment because the melting curves will be differentiated. Differentiation emphasizes noise. In order to ensure that your data analysis script effectively handles the noise you are likely to observe, simulated random and impulse noise will be added to the signals.
To simulate noise, we can use Matlab's randn function, which generates normally distributed random numbers with unity standard deviation. The two arguments tell randn to create a vector of random samples with size 1xlength(V_RTD).
noise = 0.001 * randn(1,length(sim1.V_RTD))'; % Create noise vector, standard deviation=1mV
sim1.V_RTD = sim1.V_RTD + noise; % Add simulated noise to the voltage signal
figure(8)
plot(sim1.time, sim1.V_RTD, 'r');
xlabel('Time (sec)');
ylabel('RTD Voltage (V)');
title('Simulated RTD Voltage with Noise vs. Time');
Revisit your code from DNA Melting: Simulating DNA Melting - Basics and using the approach above add noise to your RTD voltage signal, then explore the behavior of your code for different levels of noise. In particular, you can add differentiation of the curve from Figure 6 and discover the issues with attempts to differentiate that signal without additional processing. You will likely find that you first need to either sort or bin your temperature data so that the f vs T function can be differentiated. Then also run this data through your fit function and observe any difference in the fit statistics.
You are also encouraged to add noise at additional frequencies that you think might be present in the lab, then attempt to filter that data in Matlab to test the effectiveness of the RTD voltage filter design that you built in the lab. To do this, generate the noise (perhaps 60 Hz, pink noise, possibly high frequency noise from switching in the overhead lights, or even noise on the earth ground that could be coming from equipment elsewhere in the building) and add it to the signal from Figure 8. Remember it is a long way to the earth from our lab. Next filter that signal using your transfer function and the matlab command lsim. Then again run this data through your fit function.
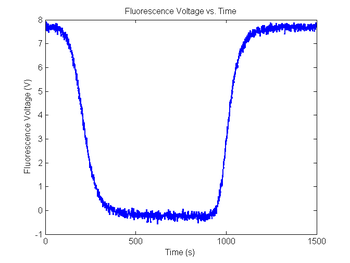
Add some noise to the sample fluorescence signal
Now that we have added noise to the RTD voltage signal, the next step is to do the same for the fluorescence signal.
The output range of the transimpedance amplifier depends on many factors, including: dsDNA quantity, illumination intensity, fluorophore efficiency, optical system gain, photodiode efficiency, and electronic amplifier gain. All of the factors except dsDNA concentration essentialy remain constant. Thus, the output of the transimpedance amplifier can be modeled by a single overall system gain factor times the dsDNA fraction. In addition, the amplifier output may be offset by a constant DC value, which is simple to model. (If the output of your apparatus drifts significantly over time, you will need to improve your implementation and methods to minimize this.)
The output range of the transimpedance amplifier over the course of an experimental run can vary depending on several factors, including the amplifier gain, optical system gain, etc... A typical setup might produce values between, say, 0.5 and 7.2 Volts. The simulation code generates two random numbers to set the range and minimum value of the data. Your data analysis script will have to normalize the amplifier output voltage to a fractional value between 0 and 1. (What assumptions will you make about dsDNA concentration to do the normalization?)
In addition to white Gaussian noise [1] (including shot noise from the photodiode and Johnson noise in your feedback resistors), the high gain amplifier sometimes produces impulse noise. This can be caused by small static discharges, for example when a charged person sits down in a chair in the lab, or by machinery switching on or off somewhere else in the building. Each of these latter noise sources would generally show up on your ground reference, even when connected to the building earth ground, an often imperfect grounding source. Your goal is first to provide as much filtering as possible in your circuitry. However, these noise sources are difficult to completely eliminate, so it is a good idea to include some filtering in your data analysis script.
Range = 5 + 4 * rand(); % Range between 5 and 9
Minimum = 2 * rand() - 1; % Minimum between +/- 1
sim1.V_f = Range * sim1.dsDnaFraction + Minimum; % Scale output
noise = 0.01 * randn(1,length(sim1.V_f))'; % Random noise, standard deviation=10mV
sim1.V_f = sim1.V_f + noise; % Add random noise
noise = rand(1,length(sim1.V_f))'; % Uniformly distributed random numbers
ImpulseNoiseProbability = 1 ./ 75; % Probability of impulse noise
noise = 20 * (noise < ImpulseNoiseProbability) - 10; % Quantize impulse noise
sim1.V_fNoisy = max(sim1.V_f, noise); % Add in impulse noise
figure(9)
plot(sim1.time, sim1.V_fNoisy)
title('Fluorescence Voltage vs. Time');
xlabel('Time (s)');
ylabel('Fluorescence Voltage (V)');
As in the last section, revisit your code from DNA Melting: Simulating DNA Melting - Basics but this time add noise to your fluorescence voltage signal, then explore the behavior of your code for different levels of noise. Then again run this data through your fit function.
Here too you are encouraged to add noise at additional frequencies that you think might be present in the lab. What could you do to minimize the effects of these noise sources? Think of solutions both at the hardware level and at the software level and model both of them.
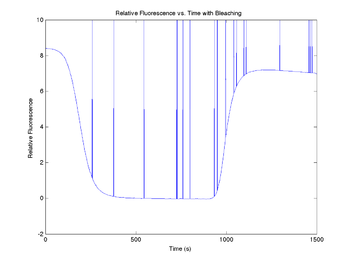
Add photobleaching effects
Each time a SYBR Green molecule is excited by a photon, there is a small chance that it will be destroyed and permanently lose its ability to fluoresce. The effect of photobleaching on the measured fluorescence intensity can be significant. To demonstrate this, a model for photobleaching may be added to the simulation. In the model, a small, fixed percentage of the fluorophores are mathematically destroyed each time sample. This can be implemented with a simple integration. The derivation of this model can be found here.
The model does not completely describe observations, so in the code below, we have also added an additional time-linear bleaching relationship that has helped to explain the observed behavior. The fraction of fluorophores destroyed per time sample is set by the variable bleachingCoefficient, while the coefficient for the linear case is bleachingConstant.
sim1.filtV_f = medfilt1(sim1.V_fNoisy,15); % temporarily remove shot noise
sim1.fluorescenceNorm = sim1.filtV_f / max(sim1.filtV_f); % normalize photo diode signal to dsDNA fraction
sim1.bleachingCoefficient = 3e-5; % 1/s, estimated from previous experiments
sim1.bleachingConstant = 3e-4; % 1/s, estimated from previous experiments
sim1.bleachingCorrection = (1 - sim1.bleachingCoefficient ...
.* cumsum(1 .* sim1.fluorescenceNorm)) ...
.* (1 - sim1.bleachingConstant .* (0:(length(sim1.fluorescenceNorm)...
- 1))'); % calclation of bleaching correction by two methods, exponetial and linear
sim1.fluorescenceBleached = sim1.fluorescenceNorm ...
.* sim1.bleachingCorrection;
Range = 5 + 4 * rand(); % Range between 5 and 9
Minimum = 2 * rand() - 1; % Minimum between +/- 1
sim1.V_fScaled = Range * sim1.fluorescenceBleached + Minimum; % Scale output
noise = rand(1,length(sim1.V_fScaled))'; % Uniformly distributed random numbers
ImpulseNoiseProbability = 1 ./ 75; % Probability of impulse noise
noise = 20 * (noise < ImpulseNoiseProbability) - 10; % Quantize impulse noise
sim1.V_fBleached = max(sim1.V_fScaled, noise); % Add in impulse noise
figure(10)
plot(sim1.time, sim1.V_fBleached)
title('Relative Fluorescence vs. Time with Bleaching');
xlabel('Time (s)');
ylabel('Relative Fluorescence');